What is SEO?
SEO is a set of practices and strategies aimed at improving a website’s visibility and ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). The main goal of SEO is to increase quality and quantity of organic (non-paid) traffic to a website by making it more relevant and authoritative for specific search queries. SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization.
Why is SEO Important?
SEO is important for several compelling reasons:
- Dominant traffic source: Organic search delivers 53% of all website traffic, making it the primary channel for most websites.
- Massive industry: The global SEO industry is projected to reach $122.11 billion by 2028, reflecting its importance and effectiveness in driving business results.
- Search-centric consumer behavior: Most consumer journeys begin with a search, whether for information, products, or services.
- Fragmented search landscape: Users search across various platforms, including traditional web search engines, social media, and e-commerce sites. For instance:
- 61% of U.S. online shoppers start product searches on Amazon
- 49% start on search engines like Google
- 32% on Walmart.com
- 20% on YouTube
- 19% on Facebook
- 15% on Instagram
- 11% on TikTok
- Competitive advantage: Higher search rankings can directly impact your bottom line by increasing visibility over competitors.
- SERP complexity: Search engine results pages are increasingly competitive, filled with various features like knowledge panels, featured snippets, maps, images, videos, and People Also Ask boxes.
- Sustainability: Unlike paid campaigns or unreliable social media traffic, good SEO work provides sustainable results over time.
- Holistic marketing foundation: SEO insights can inform and improve other marketing efforts across campaigns, website content, and social media properties.
- Trust and authority: Websites ranking well are often perceived as more trustworthy and authoritative, aligning with Google’s ranking preferences.
- Business goal achievement: SEO drives traffic that contributes to key business objectives like conversions, visits, and sales.
- Cross-platform visibility: Being “search engine friendly” is essential on any platform where people might search for your brand or business.
What Are The Benefits of SEO?
The benefits of SEO are listed below:
- Increased organic traffic: SEO drives more visitors to your site without ongoing ad spend.
- Cost-effectiveness: Once implemented, SEO can provide long-term benefits at a lower cost than continuous paid advertising.
- Improved user experience: SEO practices often align with creating a better, more user-friendly website.
- Higher conversion rates: SEO-optimized sites tend to load faster, are easier to use, and display properly on mobile devices, leading to higher conversion rates.
- Brand awareness: Higher search rankings increase visibility, recognition, and recall of your brand.
- Credibility and trust: Users often view high-ranking sites as more trustworthy and authoritative.
- Competitive advantage: Effective SEO can help you outrank competitors and capture market share.
- Local visibility: For local businesses like plumbing or cleaning services, local SEO helps attract nearby customers.
- 24/7 promotion: SEO works round-the-clock to promote your business, even outside of business hours.
- Measurable results: SEO efforts can be tracked and analyzed, allowing for data-driven improvements.
- Long-term strategy: Unlike paid ads that stop working when you stop paying, SEO benefits can last for extended periods.
How is SEO different from SEM and PPC?
SEO (Search Engine Optimization), SEM (Search Engine Marketing), and PPC (Pay-Per-Click) are all strategies used to increase visibility and traffic from search engines, but they differ in approach and execution.
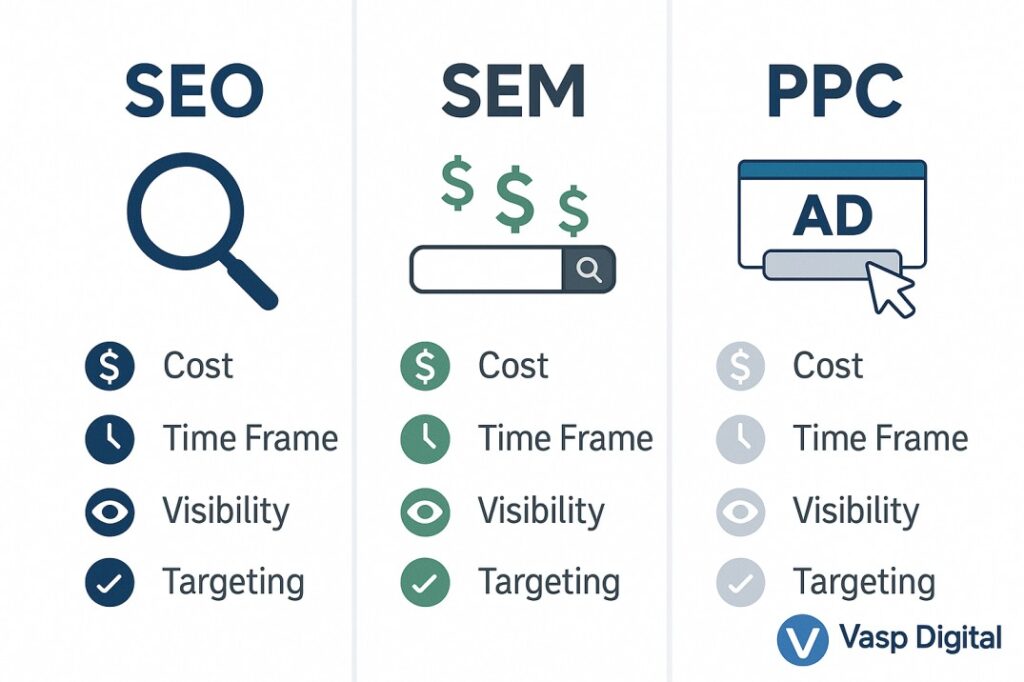
SEO vs. SEM
- Definition:
- SEO: The practice of optimizing a website to improve its organic (non-paid) ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs).
- SEM: A broader term that encompasses both SEO and paid search strategies to increase visibility in SERPs.
- Scope:
- SEO: Focuses on organic search results only.
- SEM: Includes both organic and paid search efforts.
- Cost:
- SEO: Requires time and resources but doesn’t involve direct payment for placements.
- SEM: Often involves paid advertising in addition to SEO efforts.
- Time Frame:
- SEO: Generally takes longer to see results but can provide long-term benefits.
- SEM: Can provide immediate visibility through paid ads while working on long-term SEO strategies.
- Control:
- SEO: Less control over when and where your site appears in search results.
- SEM: More control, especially with paid elements, allowing for immediate visibility in specific placements.
SEO vs. PPC
- Definition:
- SEO: Optimizing a website for better organic search rankings.
- PPC: A model of internet marketing where advertisers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked.
- Placement in SERPs:
- SEO: Aims for placement in the organic search results.
- PPC: Ads appear in designated ad spaces, often at the top or bottom of SERPs.
- Cost Structure:
- SEO: Costs are associated with optimization efforts, not placement.
- PPC: Direct costs for each click on your ad.
- Longevity:
- SEO: Results can be long-lasting and continue to provide value over time.
- PPC: Traffic stops as soon as you stop paying for ads.
- Targeting:
- SEO: Targets keywords and topics relevant to your content and audience.
- PPC: Allows for very specific targeting based on keywords, demographics, location, and more.
- ROI Timeline:
- SEO: Often takes longer to see ROI, but can provide sustained benefits.
- PPC: Can provide quick ROI if campaigns are well-managed, but requires ongoing investment.
- Flexibility:
- SEO: Changes can take time to impact rankings.
- PPC: Allows for quick adjustments to campaigns, budgets, and targeting.
What Are The Types of SEO?

The types of SEO are explained below:
Technical SEO:
Technical SEO involves optimizing the backend and technical aspects of a website to ensure that search engines can efficiently crawl, index, and rank the site. This includes improving website speed, enhancing mobile responsiveness, fixing crawl errors, implementing structured data, and ensuring secure connections through SSL.
Focus:
Optimizing the technical aspects of a website
Key elements:
• Site architecture for crawlability and indexability
• URL structure
• Navigation and internal linking
• Page speed and Core Web Vitals
• Mobile-friendliness and usability
• HTTPS implementation
• Structured data (schema) markup
• Web hosting and CMS optimization
• Site security
On-site SEO (Content Optimization):
Onsite SEO, also known as On-Page SEO, refers to the practice of optimizing individual web pages to improve their search engine rankings and drive relevant traffic. It involves optimizing content, meta tags, URLs, header tags, and internal links, as well as ensuring that the website is user-friendly and mobile-responsive.
Focus:
Optimizing the content on a website for both users and search engines
For users:
• Creating relevant, expert content
• Keyword integration
• Unique and original content
• Well-written, error-free text
• Up-to-date and accurate information
• Multimedia inclusion (images, videos)
• Content that outperforms SERP competitors
• Readable and well-structured content
For search engines:
• Title tag optimization
• Meta description optimization
• Header tags (H1-H6) usage
• Image alt text
• Open Graph and Twitter Cards metadata
Off-site SEO:
Offsite SEO, or Off-Page SEO, focuses on actions taken outside of the website to improve its authority and ranking in search engine results. This primarily includes link-building strategies, social media marketing, influencer outreach, guest blogging, and fostering positive online mentions and reviews.
Focus:
Creating brand assets and enhancing brand awareness, recognition, and demand generation
Key activities:
• Link building
• Brand building and marketing
• Public relations (PR)
• Content marketing (videos, ebooks, research studies, podcasts, guest posting)
• Social media marketing and optimization
• Listing management
• Ratings and reviews management
SEO Specialities: Niche Areas of Expertise
Ecommerce SEO:
Focuses on optimizing online stores to increase visibility and sales. Key elements include product and category page optimization, managing faceted navigation, optimizing product images and reviews, implementing schema markup for products, and creating an effective internal linking structure for large product catalogs.
Enterprise SEO:
Deals with managing SEO for large, complex websites with numerous pages. It involves developing scalable SEO strategies, automating SEO tasks, fostering cross-department collaboration, and managing multiple domains or subdomains. Enterprise SEO often requires navigating complex organizational structures and long implementation timelines.
International SEO:
Focuses on optimizing websites for multiple countries or languages. This includes implementing hreflang tags, managing country-specific domains or subdomains, creating localized content, and building international links. It also involves understanding and optimizing for different search engines popular in various regions.
Local SEO:
Aims to improve visibility for location-based searches. Key strategies include optimizing Google My Business listings, building local citations, creating location-specific content, managing online reviews, and engaging in local link building. It’s crucial for businesses serving specific geographic areas.
News SEO:
Focuses on optimizing news websites for better visibility in search engines and news aggregators. This involves creating XML news sitemaps, implementing Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP), optimizing for breaking news keywords, using structured data for news articles, and tailoring content for inclusion in Google News.
How Search Engine Optimization Works?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a complex and ongoing process that involves multiple components working together. Here’s a comprehensive look at how SEO works:
- Understanding Search Engines: SEO begins with comprehending how search engines operate. This involves four key stages:
- Crawling: Search engines use bots to discover web pages by following links and sitemaps.
- Rendering: They interpret how pages will appear using HTML, JavaScript, and CSS.
- Indexing: Content and metadata are analyzed and added to the search engine’s database.
- Ranking: Algorithms assess various signals to determine a page’s relevance and quality for specific queries.
- Comprehensive Research: Effective SEO relies on thorough research, including:
- Audience research: Understanding target demographics, psychographics, and pain points.
- Keyword research: Identifying valuable search terms and assessing demand and competition.
- Competitor analysis: Evaluating competitors’ strategies and content.
- Brand/business research: Aligning SEO with overall business goals.
- Website audits: Uncovering technical issues and opportunities for improvement.
- SERP analysis: Understanding search intent and optimizing content accordingly.
- Strategic Planning: Developing a long-term SEO strategy involves:
- Setting clear goals and milestones.
- Defining relevant KPIs and metrics.
- Deciding on implementation methods (internal, external, or hybrid).
- Coordinating with stakeholders.
- Selecting and implementing necessary tools and technologies.
- Building and training an SEO team.
- Allocating budget.
- Establishing reporting processes.
- Implementation: Putting the strategy into action through:
- Creating new, optimized content.
- Enhancing existing pages with SEO best practices.
- Removing or updating outdated or low-quality content.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Continuous vigilance is crucial. This includes tracking:
- Traffic fluctuations on critical pages.
- Page speed and responsiveness.
- Indexing status.
- Website uptime.
- Broken links and other technical issues.
- Analysis and Reporting: Measuring SEO success requires:
- Utilizing analytics tools (e.g., Google Analytics, Search Console).
- Employing specialized SEO platforms or tools.
- Regular reporting at meaningful intervals.
- Comparing performance across different time periods.
SEO is an ongoing process that adapts to changes in search algorithms, user behavior, and competitive landscapes. It requires constant monitoring, testing, and improvement to maintain and enhance a website’s visibility in search results. As the digital landscape evolves, so too must SEO strategies to ensure continued success.
What Are the Main SEO Ranking Factors on Google?
While Google’s exact ranking algorithm is complex and not fully disclosed, several key factors are known to influence how websites rank in search results:
- Content Quality and Relevance:
- High-quality, original content that addresses user intent
- Comprehensive coverage of topics with expertise and authority
- Use of relevant keywords and topics
- Technical SEO:
- Website crawlability and indexability
- Fast page load speeds and good Core Web Vitals
- Mobile-friendliness
- Secure website (HTTPS)
- Proper use of structured data
- User Experience:
- Easy navigation and intuitive site architecture
- Clear, readable content
- Absence of intrusive interstitials
- Engagement metrics (although their direct impact is debated)
- Links:
- Quality and quantity of backlinks from authoritative and relevant websites
- Internal linking structure
- E-E-A-T Signals:
- Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness of the content and website
- Author expertise and credibility
- On-Page Optimization:
- Proper use of title tags, meta descriptions, and header tags
- Image optimization (including alt text)
- URL structure
- Site Architecture:
- Logical site structure and hierarchy
- Effective internal linking
- Fresh and Updated Content:
- Regular updates to existing content
- Publishing new, relevant content
- User Intent Alignment:
- Content that matches the searcher’s intent (informational, navigational, transactional, or commercial)
- Social Signals:
- While not a direct ranking factor, social engagement can indirectly impact SEO
It’s important to note that these factors work in combination, and their importance can vary depending on the specific query and context. Google’s algorithms are constantly evolving, incorporating machine learning to better understand and rank content. Therefore, focusing on creating high-quality, user-centric content while adhering to technical best practices remains the most sustainable SEO strategy.
How to Learn SEO?
To learn SEO, follow these steps:
1.Start with the Basics:
- Understand what SEO is and its importance in digital marketing
- Learn the fundamental concepts of how search engines work
- Familiarize yourself with key SEO terminology
2. Use Trusted Resources:
- Read reputable SEO news sites like Search Engine Land
- Subscribe to our SEO newsletters for regular updates
3. Explore Google’s Resources:
- Study Google’s Search Essentials documentation
- Read through Google’s SEO starter guide
- Review Google’s Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines
4. Gain Hands-on Experience:
- Build your own website about a topic you’re passionate about
- Experiment with various SEO techniques on your site
- Observe what works and what doesn’t
5. Develop Essential Skills:
- Learn about technical SEO, on-page optimization, and off-page strategies
- Understand the importance of content creation and optimization
- Study keyword research techniques and tools
6. Stay Updated:
- Follow SEO experts on social media
- Regularly read SEO blogs and publications
- Join SEO forums and online communities for discussions
7. Attend Conferences and Events:
- Participate in SEO conferences like SMX (Search Marketing Expo)
- Attend local SEO meetups and workshops
- Engage in webinars and online SEO events
8. Take Courses and Get Certified:
- Enroll in online SEO courses (both free and paid options are available)
- Consider getting certifications from reputable SEO training programs
9. Use SEO Tools:
- Familiarize yourself with essential SEO tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console
- Explore other popular SEO tools and platforms in the market
10. Practice Data Analysis:
- Learn how to analyze SEO data and metrics
- Understand how to create and interpret SEO reports
11. Keep Learning and Adapting:
- SEO is constantly evolving, so make continuous learning a habit
- Stay informed about algorithm updates and industry changes
12. Network with Other SEO Professionals:
- Join SEO groups on social media platforms
- Participate in SEO-focused Slack channels or forums
13. Apply Your Knowledge:
- Look for opportunities to apply SEO in real-world scenarios
- Consider freelancing or internships to gain practical experience
14. Share Your Knowledge:
- Start a blog or contribute to SEO publications
- Teach others as a way to reinforce your own learning